What are the Main Sources of Nitrogen Oxides and Volatile Organic Compounds?

By identifying the primary sources of pollutants it is possible to isolate them or reduce the effects they have on our health. A particular emphasis should be placed on the different sources of nitrogen oxides, which people are primarily exposed to outside, and other VOCs that affect our indoor air quality. The most practical way to reduce dangerous emissions of VOCs and other harmful emissions, such as carbon monoxide, is with a smart indoor air quality monitor.
What’s the difference between them?
Nitrogen oxides are gases that are made from chemical reactions of nitrogen and oxygen. They are hazardous for our health, particularly in the forms of nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide, and can react with other atmospheric substances to create acid rain. Nitrogen oxide emissions can also contribute to ozone smog and particle pollution, but it is important to understand the difference between the two.
Other volatile organic compounds are a large variety of gases that are emitted from liquids or solids. They are also hazardous for our health and concentrations can be up to 10 times more common indoors. Measuring volatile organic emissions in the air is vital in ensuring our environmental protection, indoors and outdoors.
Where do they come from?
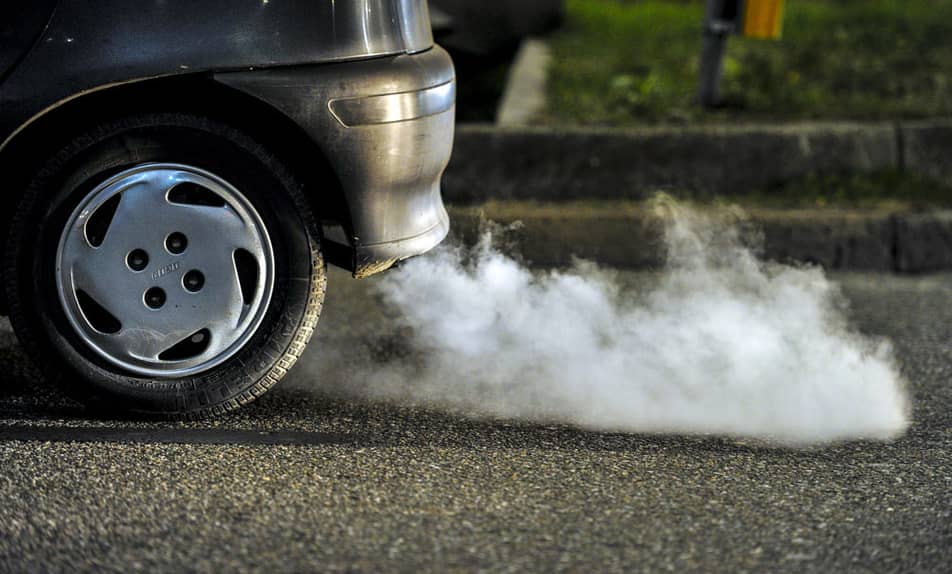
Sources of Nitrogen oxides
In high temperatures oxygen and nitrogen to merge together as a compound. Most often this happens in the combustion process of oil or coal, but more commonly in urban areas, nitrogen oxides are released through the combustion of cars and other road vehicles.
Sources of VOCs
While many VOCs have natural sources, our protection is most at risk from indoor products that use harmful chemicals in their manufacturing process. According to the EPA, the following household products emit VOCs:
-
Paints, paint strippers and other solvents
-
Wood preservatives
-
Aerosol sprays
-
Cleansers and disinfectants
-
Moth repellents and air fresheners
-
Stored fuels and automotive products
-
Hobby supplies
-
Dry-cleaned clothing
-
Pesticides
When products like wooden furnitures release harmful concentrations of VOC emissions over time, the process is often called outgassing (or off-gassing). Some of these new products may give off a strong smell when outgassing, which is often referred to as “new furniture smell”. However, not all products do this and the absence of a smell does not mean there is no danger. It is also worth noting that carbon dioxide, though considered harmful, it not actually categorized as a VOC.
Practical ways to reduce their effects
There are a number of ways to reduce or eliminate the effects of such pollutants in your home and/or workplace.
-
With a home air quality monitor, homeowners can be warned about high levels of nitrogen oxides or other dangerous atmospheric chemicals, such as ozone, and take precautions to reduce them.
-
Before purchasing new products or furniture, study the US EPA list of pollutants to know what chemicals may have a negative effect on your environmental health.
-
To further understand when VOCs emission become dangerous inside and outside, an understanding of the units used to measure volatile organic compounds is beneficial, as well as when concentrations reach their threshold value limit.
Pollution, both indoors and outdoors, can be extremely hazardous and emissions must be monitored. To ensure the safety of people’s health, it is important to locate where dangerous chemicals are emitted and reduce their impact as much as possible.
Sources
1. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/00022470.1974.10469908
2. https://toxtown.nlm.nih.gov/chemicals-and-contaminants/nitrogen-oxides
3. http://www.lung.org/our-initiatives/healthy-air/outdoor/air-pollution/ozone.html
4. http://www.lung.org/our-initiatives/healthy-air/outdoor/air-pollution/particle-pollution.html
5. https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/volatile-organic-compounds-impact-indoor-air-quality
6. https://chem.libretexts.org/Textbook_Maps/Environmental_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_(Environmental_Chemistry)/Acid_Rain/Sources_of_Nitrogen_Oxides
7. https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/volatile-organic-compounds-impact-indoor-air-quality#Sources
8. https://www.nontoxicliving.tips/blog/why-does-new-furniture-smell
9. https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/technical-overview-volatile-organic-compounds