One of the key elements of indoor air quality (IAQ) is keeping pollutant levels under control. There are many substances that degrade air quality, each generated from different sources and producing a distinct set of negative effects, ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening reactions, all of which reduce productivity in a larger or smaller scale.
This article will provide an overview of the most relevant indoor air pollutants, among the hundreds that exist, that can be found in the workplace. The smallest particles tend to be the most harmful, due to the ease with which they can penetrate human lungs – Foobot’s technology is a powerful tool for monitoring and controlling these particles, since it focuses on detecting those with sizes ranging from 0.003 to 2.5 microns, the most dangerous range, as you will discover in this article.
Particulate Matter
Particulate matter (PM) is a general term for a mixture of particles and liquid droplets that are typically found together, which includes dirt, dust, smoke and soot. Particles with a size of less than 10 micrometers are generally the most harmful, since they can be inhaled and may even reach the bloodstream. Since PM is typically generated outdoors, filtering the supply air is generally the best way to control it.
Keep in mind that PM can also be generated indoors, and in these cases it must be controlled at the source. The most common indoor sources of PM in the office are:
- Cumulated dust.
- Pollution coming through the windows and air intakes.
- Aromatic candles, incense, etc.
- Cigarette smoke.
- Combustion-based appliances: Furnaces, stoves, fireplaces, etc.
Foobot’s technology is capable of detecting PM2.5, which are also the most dangerous due to the ease with which they can spread through the alveoli in the lungs.
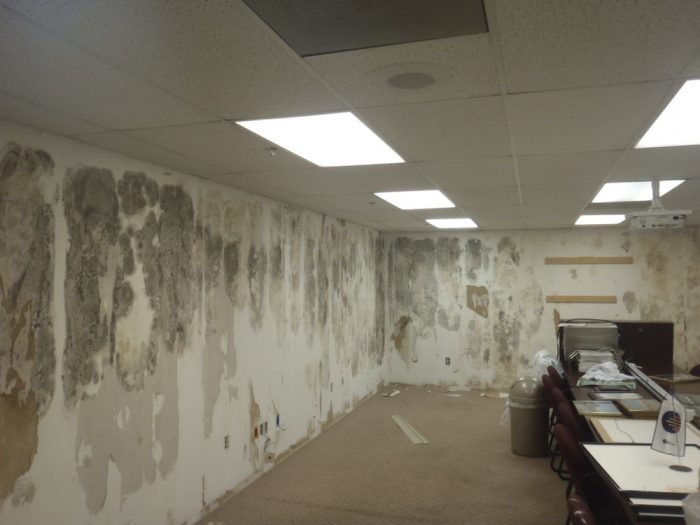
Mold & Other Fungi
Mold can trigger allergies or asthma, while causing damage to furniture, and is often found in indoor spaces with excessive humidity. Mold can be detected more easily that other pollutants due to its smell and dark color, unless it is growing hidden from sight.
A key characteristic of mold is that, being a fungus species, it reproduces my emitting spores. These spores come in a broad range of sizes, but may have diameters as small as 3 microns. Thus, they can be detected reliably by Foobot’s technology.
Mold can generally be removed, unless it has become embedded in furniture, but its spores are practically impossible to eliminate completely. The most effective way to eliminate mold is to control moisture by keeping relative humidity within the ASHRAE-recommended range of 30% to 60%.
When porous material, like furniture and some kinds of walls, becomes severely infected with mold, it must be generally discarded. You may have your maintenance team clean minor growths, as long as they wear the proper equipment, like a N95 mask, to avoid inhaling spores. However, hiring a remediation company is highly recommended in the case of severe mold infections - significant amounts of spores can be released at once when large mold growths are disturbed.
The evaporator units of air conditioning systems can also be affected with mold, since they collect moisture from indoor air; controlling mold in AC units is very important because their blowers give spores a “free ride” to other indoor areas.
Volatile Organic Compounds
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are a category of air pollutants with two key characteristics:
- They contain carbon atoms and are considered organic molecules. Just keep in mind that, while all VOCs contain carbon, the opposite does not apply - many compounds that contain carbon are not considered VOCs.
- They have a low boiling point and a tendency to evaporate at room temperature.
VOCs come from a wide variety of sources, including construction materials, furniture and office products. They are also present in many aromatizing, personal care and cleaning products that come as sprays. In addition, VOCs can also be produced by combustion appliances, or as the result of chemical reactions when indoor air contains ozone.
Many VOCs have odors, and some even have a pleasant smell. However, they are detrimental for air quality nevertheless. Aromatic plants are a far better choice if you want indoor environments to have a pleasant smell.
Since there are thousands of VOCs, this guide will concentrate on some of the most common ones. Their effects have been widely studied by organizations such as the US Environmental Protection Agency and NASA. When VOCs are monitored, their total concentration is generally measured unless a specific compound is being analyzed.
Trichloroethylene (C2HCl3)

Many printer inks contain trichloroethylene.
Trichloroethylene is a volatile organic compound (VOC), which means it has a tendency to evaporate readily when exposed to air at atmospheric pressure and room temperature.C2HCl3 is commonly found in printing inks, painting products and adhesives.
Short-term exposure to C2HCl3 produces anxiety, dizziness, headache, nausea, skin irritation and eye irritation. Increased concentrations may produce loss of consciousness and coma, with the potential to damage the heart and nervous system. There is also scientific evidence that C2HCl3 is a potential kidney carcinogen.
Trichloroethylene is colorless in both its liquid and gaseous forms, but has a smell that can be described as sweet. Thus, it is not fully undetectable by human senses, and occupants can react to the smell before the gas takes effect.
Formaldehyde (CH2O)

Most plywood, and other kinds of compressed wood, contain formaldehyde.
Formaldehyde is a VOC found in many paper products, plywood and synthetic fabrics. It is produced through oxidation or incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons - cigarette smoke and car exhaust gases typically contain formaldehyde.
CH2O is considered toxic for humans: in small amounts it causes irritation of the mouth and upper respiratory system, and exposure to high enough concentrations can cause the larynx and lungs to swell. Although the gas is colorless, it is characterized by a suffocating and pungent odor. Like many other VOCs, formaldehyde is also a carcinogen.
Benzene (C6H6)

Seemingly harmless products, like crayons, may contain toxic benzene.
Benzene is a toxic and flammable VOC, typically used as an industrial solvent. In urban settings, it is commonly found in painting products, adhesives, wax, tobacco smoke and car exhaust gases. Benzene is colorless, but can be identified by its characteristic odor similar to that of gasoline.
In small concentrations, C6H6 causes eye irritation, headaches and an increase in heart rate. Exposure to a larger dose of the gas can cause a loss of consciousness, and it is capable of damaging the central nervous system and bone marrow.
Xylene (C8H10)

Xylene is present in all kinds of markers, look for xylene-free options.
Xylene can be found in combustion gases, as well as in rubber, leather and ink products.
Xylene can irritate the mouth and throat in small concentrations, while causing confusion and headache. A large dose can induce coma, and long-term exposure can damage the kidney, heart and liver. All forms of xylene are colorless, and their odor can be described as sweet.
Pet Dander
All animals with fur or feathers release organic particles, and these may trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Even if you are not sensitive to it, make sure you clean your furniture properly because pet dander is a food source for mites, which may also trigger allergies.
If your office is pet friendly but you prefer to avoid the possible allergic reactions to pet dander, consider animals without fur or feathers, such as fish or reptiles.
Pet dander particle sizes range from 0.5 to 100 microns. Particles on the lower end of the size range are easily detectable by Foobot, especially those close to 2.5 microns in diameter.
Dust Mites
Dust mites normally live in furniture, carpets and beds, and they are a common cause of allergic reactions. They are too small to be seen by the unaided eye, with sizes ranging from 100 to 300 microns, and can float in the air when dust is disturbed, spreading throughout interior spaces.

Magnified picture of a dust mite.
Like mold, dust mites are living organisms and require humidity to survive: if you reduce humidity to the levels recommended by ASHRAE, dust mites die off. You can also capture them by using a vacuum cleaner with a high-efficiency particulate arrestance (HEPA) filter. They thrive in carpets, blankets, and furniture like desk chairs, so cleaning them frequently is highly recommended.
Note About Allergies and Absenteeism
Allergic rhinitis has been found to be the most costly cause for employee absenteeism and productivity losses in the workplace, costing almost 15 times more than absence due to coronary heart disease.
Pollen
Pollen is released by plants during their flowering season, and may cause asthma, rhinitis or other allergic reactions in some individuals. The most effective ways to avoid pollen are the following:
- Keep the windows shut during the flowering season of plants.
- Avoid flowering plants indoors.
- Filtration: make sure HEPA filters are being used for the best effect.
Ragweed is notorious for its ability to release large amounts of pollen: one plant can release over 100,000 grains per day. These pollen grains can then be carried for miles by the wind. Pollen grains are as varied as the plants that release them, with sizes ranging from 10 to 1000 microns.
Ozone (O3)

Ionizing air cleaner.
Although ozone plays a key role in protecting the Earth from outer space radiation in the upper atmosphere, it has plenty of harmful effects at ground level, especially if found in occupied spaces. The following are some common symptoms of ozone exposure:
- Shortness of breath and pain.
- Coughing and throat irritation.
- Respiratory tract inflammation.
- Complicating pre-existing conditions like asthma and bronchitis.
Some types of air filters release ozone, which defeats their own purpose: they capture other pollutants, but are replacing them with another harmful substance. If you will deploy air filters, make sure they are ozone-free.
Ionizing air cleaners, also known as plasma air cleaners, can effectively remove pollutants from indoor air but unfortunately increase the ozone concentration. Plasma cleaners ionize air particles, and in turn these charged particles attract pollutant particles, simplifying their capture and removal. However, charged oxygen ions also tend to react with each other, forming ozone.
Ammonia (NH3)
Ammonia is a compound that irritates the skin, eyes and respiratory system, and is capable of triggering sinusitis in susceptible individuals. NH3 is commonly found in cleaning products and fertilizers, and in its gaseous form it is characterized by being colorless and having a pungent smell.
Proper ventilation must be ensured when using products that contain this pollutant.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Unlike carbon dioxide, this gas is toxic for humans and causes life-threatening reactions at much lower concentrations. The maximum prolonged exposure allowed by ASHRAE is 9 ppm, and OSHA establishes the exposure limit at 35 ppm for a typical workday. Any CO concentration above 1000 ppm causes death in a few hours, and values above 10,000 ppm cause death within minutes.
Being an odorless, colorless and tasteless gas, it is impossible to detect with human senses alone, so it must be monitored with specialized sensors. Short-term exposure causes symptoms like nausea and headaches - evacuation is recommended if multiple occupants experience them at once, because there is a high chance that CO concentration has increased suddenly.
Carbon monoxide is a byproduct of combustion, which means that any combustion-based appliance must be properly vented. For example, boilers fired by natural gas or propane both emit carbon monoxide.
Remember
Make sure indoor air intakes are properly isolated from parking areas as these are important sources of noxious combustion byproducts like Particulate Matter (PM), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2), and Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2).
Radon
Radon is a radioactive gas that is emitted from the ground naturally, and its concentration can vary drastically from building to building. Long-term exposure to radon can have severe health effects on humans, and the gas is considered just as harmful as cigarette smoke, with the difference that it is odorless and colorless.
The best way to control radon is hiring a professional remediation company to carry out long-term monitoring. Single measurements are generally not enough to test indoor spaces for radon, given that its concentration varies throughout the year.
Lead
Lead is toxic for humans, and in buildings it is commonly found in paint and gasoline, although its concentration in these products has been decreased worldwide thanks to strict regulation by environmental and health protection agencies.
If your office is located in an area where waste incineration, mining operations and battery manufacturing activities are taken place, take measures as these also release significant amounts of lead into the atmosphere.
Long-term exposure to the metal is associated with damage to the nervous system, kidneys, bone marrow and gastrointestinal tract. Children are particularly vulnerable to lead, since it can affect the normal development of many body systems.
Arsenic

Arsenic is naturally present in tobacco leaves.
Arsenic and many of its compounds are carcinogenic and highly toxic for humans, capable of severely damaging the nervous system and leading to cardiovascular disease with prolonged exposure.
In gaseous form, Arsenic is transparent and characterized by a garlic-like odor. It is important to note that cigarettes have a high Arsenic content, and thus smokers are exposed to significantly higher concentrations than non-smokers.
Sadly, this higher Arsenic concentration, among other poisonous substances, also pollutes your office even if you banned smoking in your premises, as a consequence of thirdhand smoke.
Asbestos

Office ceiling tiles may be a source of asbestos you didn’t think of.
Asbestos is generally released in large amounts when buildings are renovated or demolished, and long-term exposure to the material can lead to respiratory diseases, especially if the patient is also a smoker.
The best way to avoid exposure to asbestos is hiring qualified professionals for any building renovation where it must be manipulated. Many building materials that have already been banned due to their asbestos content can still be found in older buildings. Find out about your office’s construction materials to avoid the hazards of long-term exposure.
Make The Invisible, Visible
After reading this comprehensive guide, you now have the knowledge to tackle the emission of the most important pollutants within your office. However, air supply comes from the outdoor, and, you sure have many other things to think about as to be all day dealing with indoor air quality, even though it’s critical for our health and productivity.
In order to make it easier for you, and help you save time and money, at Foobot, we have designed a technology that not only is capable of automatically monitoring your office air quality 24/7, but also of controlling your HVAC system in order to counteract spikes of some pollutants, humidity, temperature, or occupancy, and more. This way your office will breathe a healthier air, see productivity levels increase and energy bills tank. Learn more here.

